Update time : 2020-11-11 Publisher:Tongda
1. Fever Phase:
In the initial stage of compost production, the microorganisms in the compost are mainly of medium temperature and aerobic species, and the most common ones are non-spore bacteria, spore bacteria and molds. They start the composting fermentation process, decompose easily decomposable organic substances (such as simple sugars, starch, protein, etc.) under aerobic conditions, generate a lot of heat, and continuously increase the composting temperature from about 20°C to 40°C. It is the fever stage, or the middle temperature stage.
2. High Temperature Stage:
With the increase of temperature, thermophilic microorganisms gradually replace the mesophilic species and play a leading role. The temperature continues to rise, generally reaching above 50°C within a few days, entering the high temperature stage. In the high temperature stage, thermoactinomycetes and thermogenic fungi become the main species. They strongly decompose the complex organic substances in the compost (such as cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin substances, etc.), accumulate heat, and the compost temperature rises to 60-70°C, even as high as 80°C. Then most of them are hot. Microorganisms also die in large numbers or enter a dormant state (above 20 days), which plays an important role in accelerating the maturity of compost. Improper composting has only a short period of high temperature, or it does not reach high temperature at all, so it matures very slowly, and cannot reach a semi-ripe state in half a year or longer.
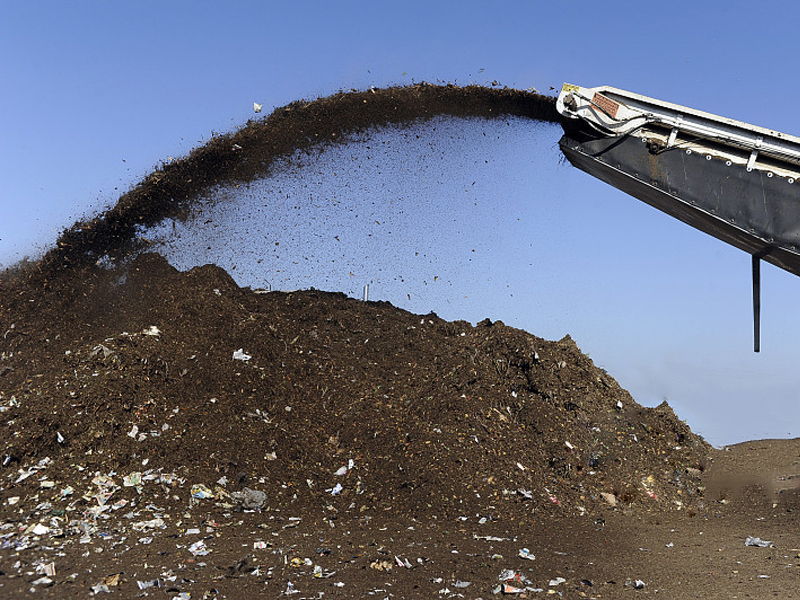

3. Cooling Stage:
When the high temperature stage lasts for a certain period of time, most of the cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin substances have been decomposed, leaving complex components that are difficult to decompose (such as lignin) and newly formed humus, and the activity of microorganisms is weakened , The temperature gradually drops. When the temperature drops below 40°C, mesophilic microorganisms become the dominant species again
If the cooling stage comes early, it indicates that the composting conditions are not ideal and the plant material is not fully decomposed. At this time, you can turn over the pile and mix the accumulated materials to make them generate a second heat and temperature to promote the maturity of the compost.
4. Decomposing and Fertilizer Maintaining Stage:
After the compost is decomposed, its volume shrinks and the temperature of the compost drops slightly higher than the temperature. At this time, the compost should be compacted to cause an anaerobic state and weaken the mineralization of organic matter to facilitate fertilizer retention.

see details +
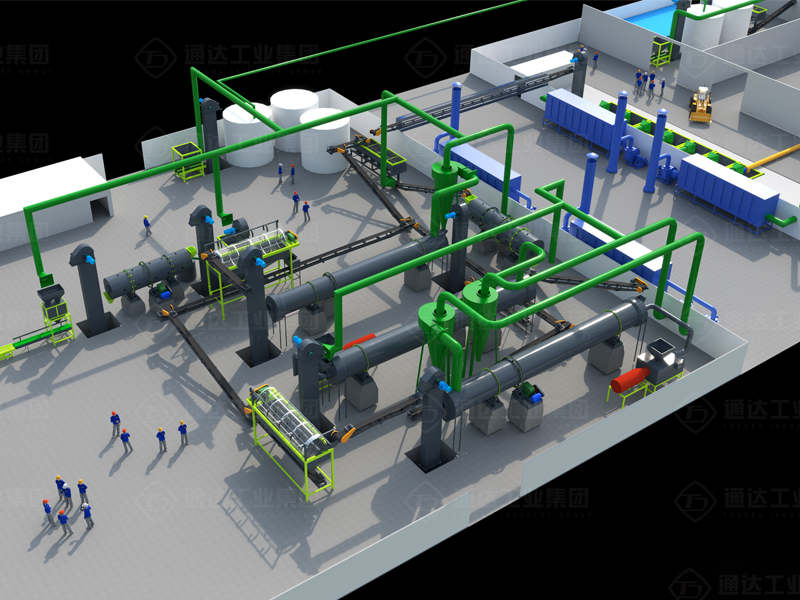
see details +
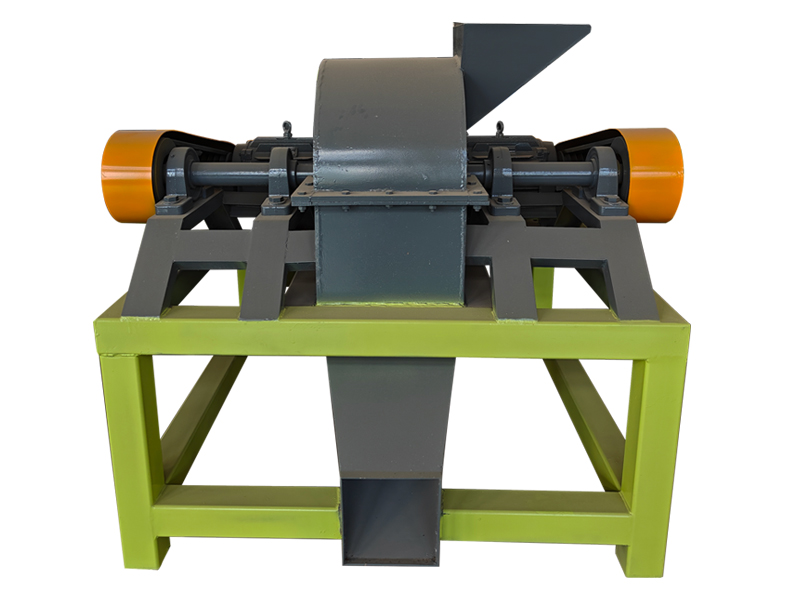
see details +

see details +

Fermentation Compost Equipment >
 Tel:+86 18538527111
Tel:+86 18538527111
 E-mail:[email protected]
E-mail:[email protected]
 Address:Longgang Development Zone Of Xingyang City, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China.
Address:Longgang Development Zone Of Xingyang City, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China.
Privacy Policy Copyright © Henan Tongda Heavy Industry Science And Technology Co., Ltd.